Overview
Description
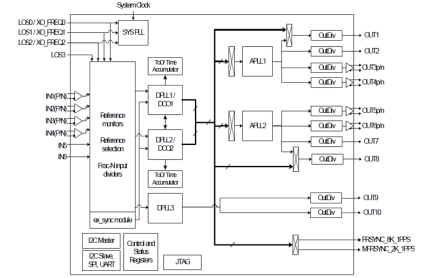
The 82P33914 Synchronization System for IEEE 1588 is comprised of software and hardware designed to meet the needs of IEEE 1588 slave clock and master clock applications. The system includes a clock recovery servo software (Servo) that runs on an external processor and Synchronization Management Unit (SMU) hardware. The Servo recovers accurate and stable electrical synchronization signals from packet-based references generated by IEEE 1588 masters. The Servo is capable of filtering the effects of Packet Delay Variation (PDV) often present in IEEE 1588 unaware networks.
The SMU hardware provides tools to manage timing references, clock sources, and timing paths for IEEE 1588 and Synchronous Ethernet (SyncE) based clocks. The device supports up to three independent timing paths that control: IEEE 1588 clock synthesis; SyncE clock generation; and general-purpose frequency translation. The device supports physical layer timing with Digital PLLs (DPLLs) and it supports packet-based timing with Digitally Controlled Oscillators (DCOs). Input-to-input, input-to-output and output-to-output phase skew can all be precisely managed. The device outputs low-jitter clocks that can directly synchronize Ethernet interfaces; as well as SONET/SDH and PDH interfaces and IEEE 1588 Time Stamp Units (TSUs).
The 82P33914-1 is no longer recommended for new designs. The only difference between the 82P33914-1 and the 82P33914 is that the 82P33914-1 relied on a proprietary PTP stack, whereas the 82P33914 relies on the Linux PTP stack, which is open source.
For more information or to request documentation, contact your local Renesas sales representative.
Features
- Includes clock recovery servo software, and Synchronization Management Unit (SMU) hardware
- Implements ITU-T Telecom Profiles
- Operates as IEEE 1588/PTP slave or master
- Recovers accurate and stable synchronization signals from packet-based IEEE 1588/PTP master
- Reference trackers filter packet synchronization noise from IEEE 1588 unaware networks
- PTP clocks comply with ITU-T G.8273.2 and G.8263
- Physical layer clocks comply with ITU-T G.8262 for Synchronous Ethernet Equipment Clock (EEC), G.813 for Synchronous Equipment Clock (SEC), and Telcordia GR-253-CORE for Stratum 3 and SONET Minimum Clock (SMC)
- System-wide precise 1PPS (Pulse Per Second) time of day alignment is supported with programmable input-to-input, input-to-output and output-to-output phase delays: sub-ns resolution
- Generates clocks for Ethernet, SONET/SDH and PDH interfaces: jitter generation <1ps RMS (12kHz to 20MHz)
- Eases local oscillator sourcing by supporting any of eight common TCXO/OCXO frequencies for the system clock: 10MHz, 12.8MHz, 13MHz, 19.44MHz, 20MHz, 24.576MHz, 25MHz, or 30.72MHz
- 72-pin QFN package
- Supported by Renesas' Timing Commander Software
Comparison
Applications
- Access routers, edge routers, core routers
- Carrier Ethernet switches
- Multiservice access platforms
- PON OLT
- LTE eNodeB
- ITU-T G.8265.1 and G.8275.1 Telecom Profile clock synthesizer
- ITU-T G.8273.2 Telecom Boundary Clock (T-BC) and Telecom
- Time Slave Clock (T-TSC)
- ITU-T G.8264 Synchronous Equipment Timing Source (SETS)
- ITU-T G.8263 Packet-based Equipment Clock (PEC)
- ITU-T G.8262 Synchronous Ethernet Equipment Clock (EEC)
- ITU-T G.813 Synchronous Equipment Clock (SEC)
- Telcordia GR-253-CORE Stratum 3 Clock (S3) and SONET Minimum Clock (SMC)
Design & Development
Software & Tools
Models
ECAD Models
Schematic symbols, PCB footprints, and 3D CAD models from SamacSys can be found by clicking on products in the Product Options table. If a symbol or model isn't available, it can be requested directly from the website.

Product Options
Applied Filters:
Videos & Training
News & Blog Posts
| A Reference Design Saved My Bacon | Blog Post | Apr 27, 2018 |
| IDT Introduces Timing Solutions for Cavium Processors | News | Dec 18, 2017 |
| IDT’s New IEEE 1588 Hardware and Software Solution Eases Compliance with Latest Network Synchronization Standards | News | Oct 26, 2015 |