Learn how to decide if a low powered linear regulator or highly efficient switching regulator is a better option for your design.
Linear Regulators
Linear regulators are a great choice for powering very low powered devices or applications where the difference between the input and output is small. Even though they are easy to use, simple and cheap, a linear regulator is normally inefficient.
The equation for dissipated power in a linear regulator is:
Power dissipation = (input voltage – output voltage) × load current
Switching Regulators
Switching regulators on the other hand are highly efficient and available as modular chips which are compact and reliable. Switching regulators can be further divided into isolated and non-isolated.
How do you choose?
| Linear Regulator | Switching Regulator | |
|---|---|---|
| Design Flexibility | Buck | Buck, Boost, Buck-Boost |
| Efficiency | Normally low to medium-high for low difference between VIN-VOUT | High |
| Complexity | Low | Medium to high |
| Size | Small to medium, larger at high power | Smaller at similar higher power (depending on the switching frequency) |
| Total Cost | Low | Medium to high – external components |
| Ripple/Noise/EMI | Low | Medium to high |
| VIN Range | Narrow (depending on power dissipation) | Wide |
Linear Regulators
Linear regulators use linear, non-switching techniques to regulate the voltage output from the power supply. The regulator’s resistance varies according to the load and results in a constant output voltage.
All linear regulators require an input voltage at least some minimum amount higher than the desired output voltage. That minimum amount is called the dropout voltage. A low-dropout or LDO regulator is a DC linear regulator which can regulate the output voltage even when the supply voltage is very close to the output voltage.
Linear regulators are a great choice for powering very low powered devices or applications where the difference between the input voltage and output voltage is small. They are a simple and cheap solution, but linear regulators are normally inefficient because the difference between the input voltage and regulated output voltage is continually dissipated as heat.
Renesas’ low-dropout regulators (LDOs) generate low current, well-regulated outputs and require very few external components.
Renesas' Advantages
Small package, small dropout, fast transient response, high accuracy
Positives:
Simple, Low Cost, Low Noise
Negatives:
Less Efficient, Power Dissipation, Power Capacity
Switching Regulators
Some of the key requirements of today’s power management solutions include less power consumption under various load conditions, less space, high reliability and wide input voltage. These requirements are driving the need for highly efficient, wide VIN, low quiescent current (IQ) switching regulators in a broad range of applications.
Switching regulators rapidly switch a series element on and off. They can operate with both synchronous and non-synchronous switches (FETs). These devices store the input energy temporarily and then release that energy to the output at a different voltage level. The switch’s duty cycle sets the amount of charge transferred to the load.
Switching regulators are efficient because the series element is either fully conducting or switched off so it dissipates almost no power. Switching regulators are able to generate output voltages that are higher than the input voltage or of opposite polarity, unlike linear regulators. The versatility of these converters allow configuration for buck, boost, buck-boost, flyback, inverting in isolated and non-isolated applications.
Integrated FET regulators are a subset of switching regulators. These microcircuits have integrated the power MOSFET and are considered a whole solution; whereas controllers employ external power MOSFETs. Both configurations are classified as switching regulators because they regulate the output voltage.
Renesas' Advantages
Wide input and output range, integrated FETs, pin-to-pin compatible parts, internal compensation, light load efficiency mode, simple and easy to use.

Positives:
Efficient, High Power
Negatives:
Noisy, Complicated
Power Savings Between LDO and Switching Regulators
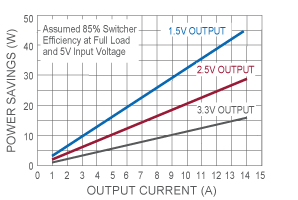
Efficiency Curve for LDO and Switching Regulators

Find a Linear or Switching Regulator
Linear Regulators
Renesas' standard and low-dropout (LDO) regulators provide a variety of simple, low cost and low noise solutions.
Switching Regulators
Renesas offers a wide range of step-down (buck), buck-boost, and step-up (boost) switching regulators that operate with both synchronous and non-synchronous internal switches (FETs).