Overview
Functional safety of electrical, electronic or programmable electronic systems is a key feature and becoming more and more important in the field of automotive due to the significantly increasing number of these systems in a modern car. Electronic Systems support the human driver or can even take over critical tasks to control the vehicle. This leads to increased risks from systematic failures and random hardware failures of these systems. ISO 26262 is the related standard for the automotive industry to provide guidance to mitigate these risks. This serves as a helpful framework for developers of automotive safety-related systems.
Together with our customers around the world and as the holder of a top-level global share in the automotive semiconductor business, Renesas has introduced state-of-the-art functional safety technologies. We are actively participating in ISO 26262 working groups and other standardization activities to lead the development of functional safety technologies globally. Leveraging our core competencies of the vast experience gained through these activities and our proven track record recognized by our many customers, we propose new system solutions that are optimized to our customers' systems and that can easily satisfy functional safety requirements to efficiently achieve compliance at the system level.
The majority of Renesas safety products are developed as Safety Element out of Context (SEooC), and this means they are not particularly developed for one specific item. The products are targeting a wide range of applications considering the appropriate level of abstraction to seamlessly fit into customers’ systems. There is a wide range of ISO 26262 compliant products available for RH850, R-Car and MSIG.
Renesas' Contribution to the Standardization of Functional Safety
Renesas strongly contributes to relevant standards and is an active member of several working groups, responsible for the development of safety standards, for over 15 years, including ISO 26262 from the genesis of the standard development:
International groups
- Expert membership in ISO WG08 (ISO26262, ISO21448)
- Working member in TC 65/SC 65A/MT 61508-1-2 for IEC 61508 maintenance
- Voting member in SAE (Functional Safety Committee and On-Road Automated Driving)
- STP member in UL4600
- Member of Independent Safety Assurance group from IET
Local groups
- Japan: JSAE, Jaspar
- UK: BSI
- Germany: DKE
Process for Compliant Development
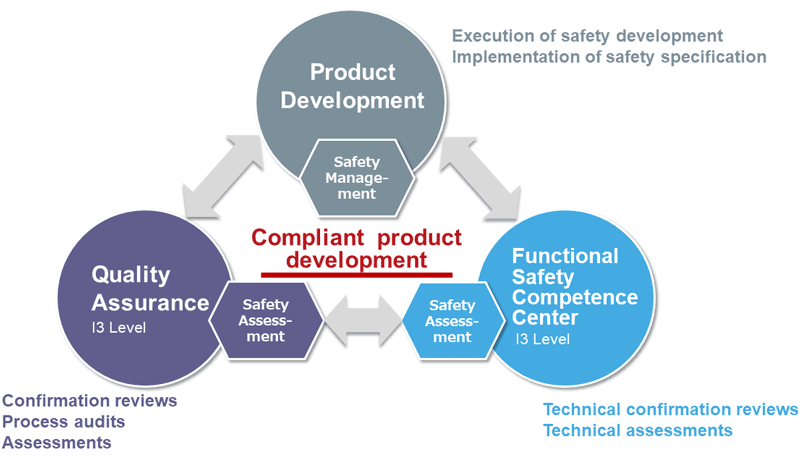
In addition to Renesas mature quality processes for automotive, Renesas has established and integrated Hardware and Software development process meeting ISO 26262 requirements for up to ASIL D compliant product developments.
This integrated development process for ISO 26262 is the base for each product development considering shared and sufficiently independent responsibilities of functional safety experts which fosters the way for inhouse functional safety assessments.
Renesas Functional Safety Support Program for Automotive Products
The "Renesas Safety Support Program for Automotive" includes different aspects for hardware and software products designed to be used in safety applications, such as the delivery of necessary safety work products according to ISO 26262 and direct support of customers by means of safety workshops.

Safety engineers at customers can rely on Renesas standard functional safety deliverables which can be made available under Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA) for dedicated products, these are safety work products according to ISO 26262, such as:
- Development Interface Agreement / Report (DIA/DIR)
- Safety Requirement Specification (SRS)
- Safety Application Note (SAN)
- Failure Mode, Effects and Diagnostics Analysis (FMEDA)
- Safety Case summary (SC)
- Functional Safety Assessment Report summary (FSA)
Functional safety technical support and workshops can be offered to customers on demand by a global team of Functional Safety experts.
Depending on each product’s safety concept and architecture, Renesas also provides Software developed as SEooC like MCAL, Software-based test libraries, Runtime Test Libraries, device driver libraries and middleware.
